SafetyNet is not something new, although lately its name has come up on the occasion of terminals launched without Huawei’s Google services. However, What is this SafetyNet and what is it for?
First we will see what exactly this security test is and what it is used for, and then tell you how can you see if your mobile passes the test and what cases can cause a mobile to fail the test.
What is SafetyNet and what is it for?
 Diagram of the operation of Safety Net, which sends the information of the device to Google servers to obtain the answer
Diagram of the operation of Safety Net, which sends the information of the device to Google servers to obtain the answer Google define SafetyNet como unos services and API to avoid abuse. Application developers can use this API to determine if the connection to the servers is genuine, from a genuine application and on a genuine device.
SafetyNet is a system that app developers have to check if the device is genuine, without modifications
I mean, what it does is check device hardware and software to verify that its integrity has not been compromised, comparing the current state with the reference data collected during the compatibility test (CTS).
It is not a DRM or strict anti-cheat system for games, but rather of a system integrity check which compares that the system remains the same as when it passed the compatibility tests. These tests are made up of a multitude of small tests to detect incompatibilities and that cover areas such as permissions or interaction between different APIs.
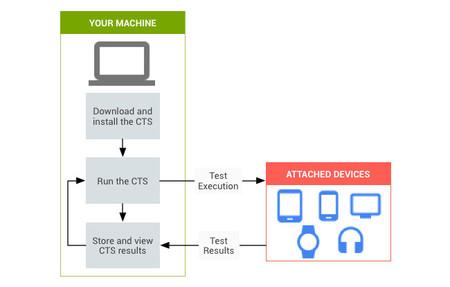 Android CTS compatibility test scheme
Android CTS compatibility test scheme It is also not a root detector, even though rooted devices will not pass the test. This is because the results returned by SafetyNet are ambiguous and are limited to saying whether the test has passed or not, but not for what reason.
Regarding its use, SafetyNet is used by developers to check overall system safety. It is these developers who must implement it in their applications and act accordingly.
For example, a bank application may not work unless the device passes SafetyNet. In fact, it already happens with Google Pay. Other developers may choose directly not show your apps on Google Play on devices that fail the test, as with Netflix.
How to know if your mobile passes SafetyNet
The easiest way to check if your mobile passes the SafetyNet check is to install an app that does the checking. There are several on Google Play that fulfill the task, the most popular being the simple SafetyNet Test.
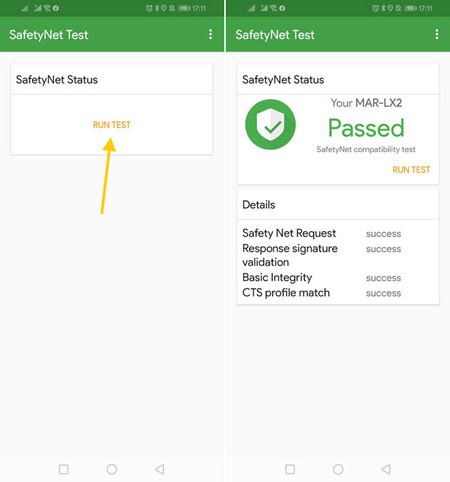
The app literally has a single button, so all you have to do is tap on Run test. The test in question takes a second and shows very clearly if it has been passed or not. Some additional details are listed at the bottom of the window.
-
Safety Net Request. It is the request for the test itself. If it is not carried out, the test is not even carried out (for example, if you do not have an Internet connection).
-
Response signature validation. It is the validation of the test result, which comes from Google’s servers.
-
Basic integrity. It is the basic integrity test, somewhat more permissive than the following. Developers can determine if they want their apps to continue working by passing at least this level of integrity.
-
CTS profile match. It is the strictest test, which only comes true when the device is established as genuine and certified according to the CTS certification.

SafetyNet Test
Why the test may fail
As we mentioned before, the SafetyNet test does not help developers know with certainty if your mobile is rooted or what is wrong with it, but rather returns true or false, without explaining why. Now, the reasons why it returns true or false are specific and are the following:
|
Test “CTS Profile Match” |
Test “Basic Integrity” |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Certified and genuine device according to CTS |
True |
True |
|
Certified device with bootloader unlocked |
False |
True |
|
Genuine uncertified device (because the manufacturer has not certified it) |
False |
True |
|
Device with custom ROM, no root |
False |
True |
|
Emulator |
False |
False |
|
It is not a device but a script |
False |
False |
|
Signs of a compromised system, such as a rooted system |
False |
False |
|
Other signs of seizures |
False |
False |
Thus, the test itself consists of two levels and can fail for all of the above reasonsHowever, the testing application will not know exactly what the case is, but only that it failed.
This means that the strictest test will fail if the device has an unlocked ROM or bootloader, although the basic integrity test is somewhat more permissive and will pass in the previous cases. What they both agree on is root: a device rooted or with similar modifications does not pass any of the tests.