After “why the chicken crossed the road”, the second great question of humanity is why your mobile does not let you download applications or take photos if memory card still has available space, an enigma that has frustrated many Android users for years.
It doesn’t seem to make any sense, and yet there is a logical explanation so that the memory of your Android mobile will resist updating or downloading new applications or taking photos. Here we will see why it happens, and what you can do about it.
Not all storage is the same
To understand why this happens, we first have to understand the concept of data partitions. A partition is nothing more than a virtual partition of a physical disk drive. The storage of an Android mobile is located divided into multiple partitions.
The number and type of partitions can vary from one mobile to another (for example, Huawei started using the EROFS read-only file system in the latest versions of EMUI), but something that most mobile phones agree on is in three partitions: system, data and cache. You can check the partitions of your mobile with applications like DiskInfo.
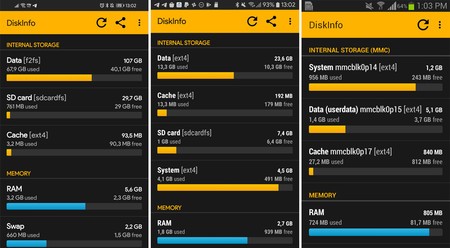 The main partitions of three Android phones
The main partitions of three Android phones There are actually a lot of additional partitions, but those are the main ones. In the system partition is the operating system and pre-installed applications, in the cache the application cache and on the data partition, the rest, including everything that is saved in the internal memory of the phone.
This is the reason why mobiles have a storage available to users considerably less than total (In the previous screenshots, 107/128 GB, 23.6 / 32 GB and 5.1 / 8 GB respectively). It is also the reason why the mobile does not stop giving you space problems despite the fact that the memory card is almost empty.
The main problem is that Android saves the data of the applications and the cache in the internal memory
The space on the memory card goes separately, but there is a problem: application data is saved in internal memory, including application downloads from Google Play and their subsequent installation. For this reason, Google Play may tell you that you do not have available space even though the memory card has free gigabytes and gigabytes.

The only thing that is saved on the memory card directly – and depends on the configuration of the camera application – are the photos and videos. The problem is that these photos and videos generate thumbnails and cache in the internal memory, so that, in the long run, even though the photos are saved on the memory card, they also have an impact on the internal memory. .
 The internal memory is used for almost everything and when it is full the problems begin
The internal memory is used for almost everything and when it is full the problems begin That is, no matter how much available space you have on the memory card, Android continues to use internal memory almost exclusively for all your needs, from downloads to saving application data and cache. The photos you take on the memory card are also noticed in the internal memory in the form of cache or data in the Google Photos app.
What can you do if you don’t have space
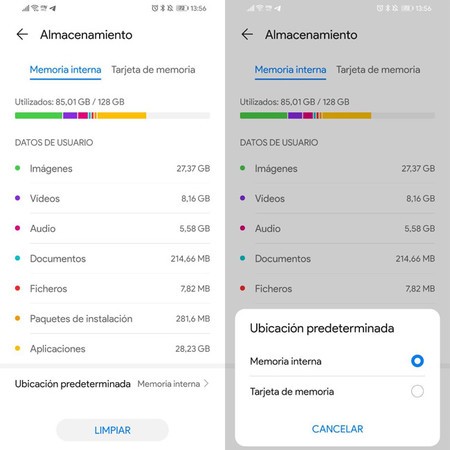 EMUI lets you choose the default storage location, although this is not normal
EMUI lets you choose the default storage location, although this is not normal If you have a memory card full of space but the internal memory is full, your mobile will not stop giving you errors every time you try to do anything. Luckily, there are a number of strategies you can carry out:
-
Free up space on your mobile. It is the most effective way to bring your mobile back to life, and it ranges from uninstalling applications to deleting files or deleting photos or videos that no longer interest you. Of course, those photos and videos that are in the internal memory.
-
Use Adoptable storage, if available. Adoptable storage is an Android function that allows you to format a memory card as if it were internal memory. It is a simple process, but unfortunately it is not available on all mobile brands. It is important to use a memory card at high speed and to remember that you will lose your portability. Come on, you will not be able to read its content on another device.
-
Choose microSD card as standard storage. It is not a standard Android feature, but some manufacturers, such as Huawei and to a lesser extent Samsung, allow you to choose the default storage location between internal memory or microSD.
-
Move apps to SD card. Moving apps to the SD card was very popular a few years ago and some layers of customization bring the option right from the settings. It is not a panacea, but in specific cases it can help rescue a few megabytes of internal memory.
-
Switch to lightweight apps. If none of the above has worked, you can try using lightweight applications and reduced versions of applications that you use such as Facebook, Messenger or Twitter.